Table of Contents
Introduction to Uttarakhand
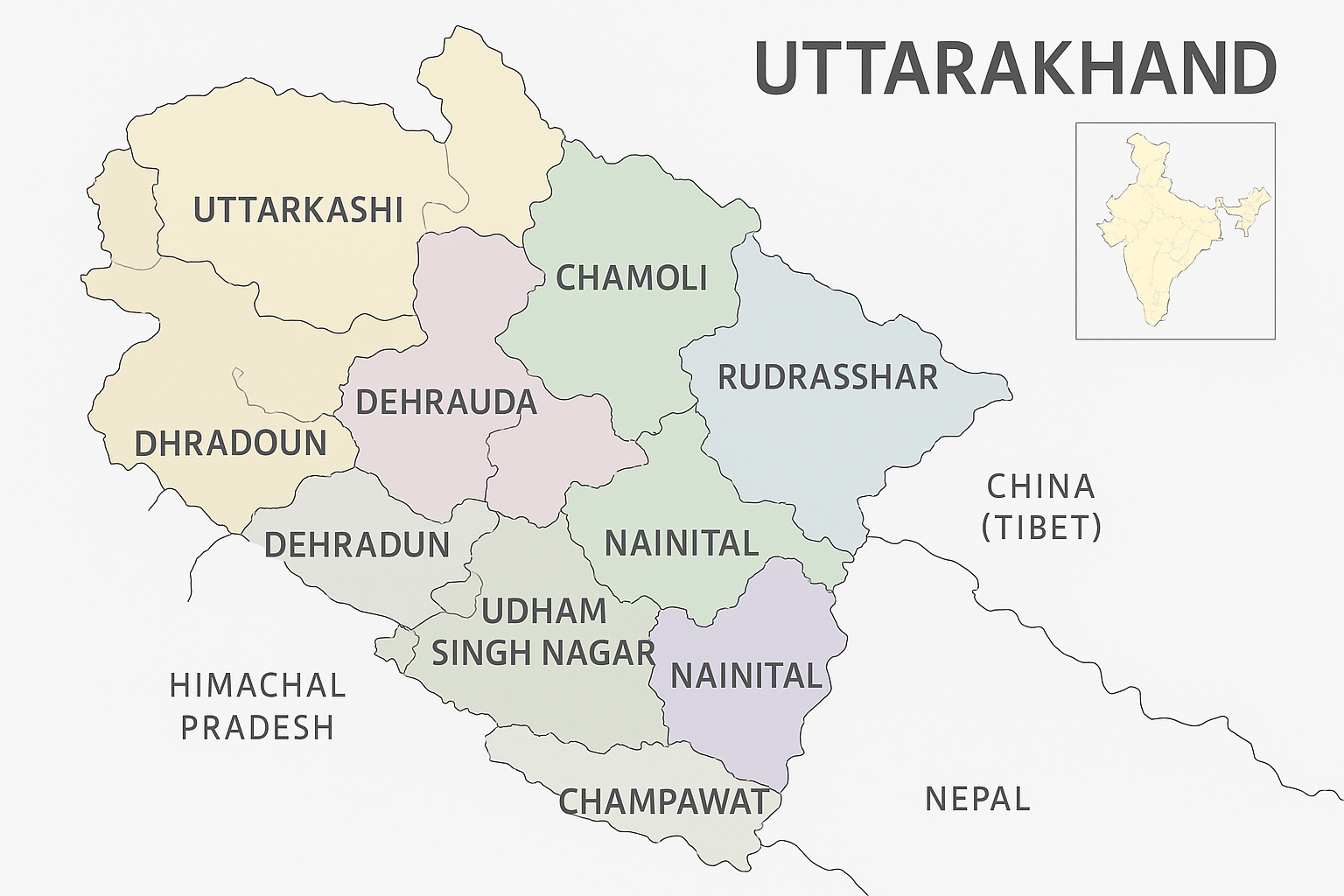
Uttarakhand, located in the northern region of India, presents a unique blend of geographical diversity and cultural richness. Bordered by Himachal Pradesh to the west and Uttar Pradesh to the south, this state has gained recognition for its breathtaking landscapes, making it a prominent travel place for both domestic and international tourists. The significance of the Uttarakhand map extends beyond mere navigational purposes; it reflects the state’s ecological diversity, historical heritage, and demographic distribution.
The state is divided into two primary regions: Garhwal and Kumaon. Each region showcases its own distinctive traits, including various mountain ranges, rivers, and valleys, which are integral to understanding the overall layout as depicted in the Uttarakhand map. The Garhwal region is known for its majestic peaks, such as Nanda Devi and Kedarnath, while Kumaon boasts the serene Naini Lake and the majestic peaks of Pindari Glacier. Such geographical features not only attract nature enthusiasts but also serve as key locations within popular Uttarakhand tourist places.
Historically, Uttarakhand has served as a significant pilgrimage destination, with ancient temples and sacred sites such as Haridwar and Rishikesh, which hold great cultural importance for Hindus. These areas are intricately marked on the Uttarakhand map, highlighting their relevance to both spiritual seekers and tourists. The valley’s rich flora and fauna, along with its intricate ecosystems, underscore Uttarakhand’s ecological significance, making it a subject of study for researchers and environmentalists alike.
In essence, Uttarakhand’s geography is not only a map outlining physical features but a testament to its cultural and ecological value. This overview sets the foundation for further exploration into the myriad opportunities for travel and research that the state offers, fueled by its diverse landscapes and rich heritage.
Understanding the Uttarakhand Map: Key Features
Uttarakhand is a state known for its diverse landscape, which is effectively illustrated through the Uttarakhand map. It showcases the physical geography, including the remarkable Himalayan mountain ranges, lush valleys, and several major rivers that define the region. The geography of Uttarakhand is not only a visual representation but serves various purposes for travelers looking for tourist places and adventure activities.
On the Uttarakhand map, the prominent mountain ranges such as the Garhwal and Kumaon Himalayas can be easily identified. These ranges are home to several significant peaks, including Nanda Devi, which stands as the second-highest peak in India. The blue lines indicating rivers like the Ganges and Yamuna reflect vital waterways that contribute to the state’s ecology and culture. A traveler studying the map can discern the proximity of these rivers to major towns and pilgrimage sites, which is crucial for those planning their travel routes.
The map also employs symbols to denote national highways, state roads, and railways, making navigation easier for visitors. Understanding these symbols allows tourists to identify key travel places effectively. Furthermore, the presence of marked temples and significant religious sites, such as the Badrinath and Kedarnath temples, on the map highlights the historical and spiritual importance of the region. Pilgrimage routes are illustrated, serving as a guide for those embarking on spiritual journeys.
In essence, the Uttarakhand map is a comprehensive tool that provides insights into the state’s geographical features, enhancing the travel experience. Its detailed representation of natural features, historical landmarks, and modern infrastructure not only assists in navigation but also fosters appreciation for the rich cultural heritage of Uttarakhand.
Tourism and Natural Attractions Identified on the Map
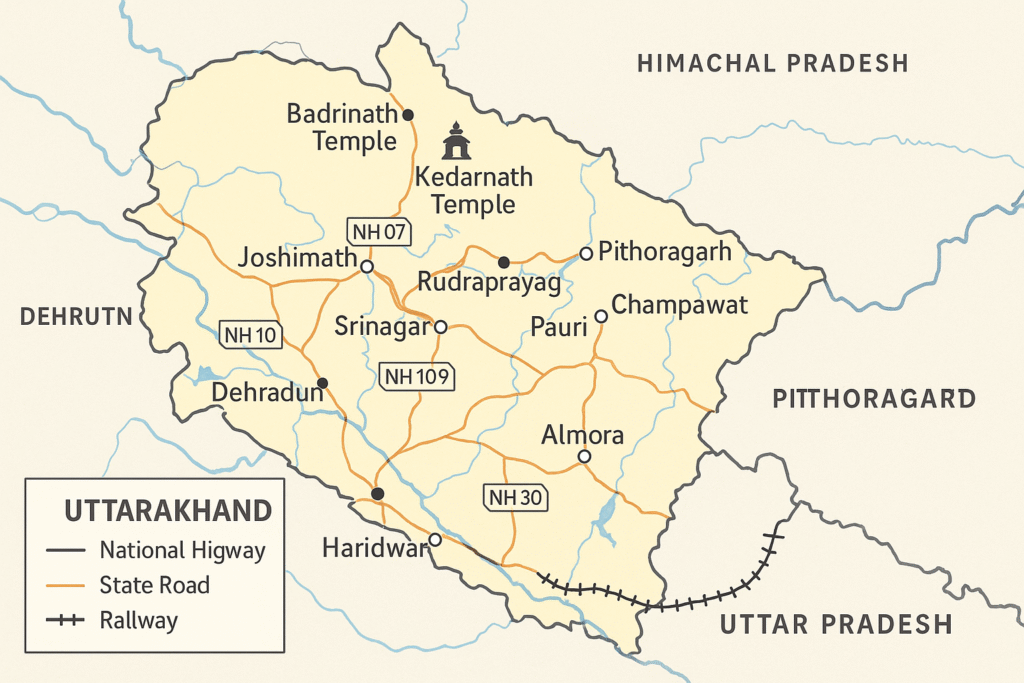
Uttarakhand, known for its breathtaking landscapes and serene environments, is a prime travel destination that has much to offer. The Uttarakhand map serves as an essential tool for visitors, highlighting both popular and hidden gems throughout the region. Among the standout Uttarakhand tourist places are hill stations such as Nainital, Mussoorie, and Ranikhet, each boasting unique attractions and scenic views. The well-marked paths on the map indicate the best routes to reach these enchanting locations, helping travelers navigate the mountainous terrain effectively.
In addition to hill stations, the state is home to several renowned national parks, including Jim Corbett National Park and Rajaji National Park. These parks are not just significant tourist spots but also rich biodiversity havens. The Uttarakhand map assists travelers in accessing various entry points and recommended trails, enhancing their experience of wildlife exploration. Lakes like Bhimtal and Naukuchiatal, which offer tranquility and adventure sports, are also crucial markers on this map, attracting visitors seeking leisure and recreation.
For enthusiasts looking to venture off the beaten path, the Uttarakhand map can reveal lesser-known trek routes, such as the trails leading to Kedartal or the paths surrounding Auli. These areas are often overlooked, yet they provide some of the most stunning views and authentic experiences of Uttarakhand’s natural beauty. By utilizing the map, travelers can enrich their journey, ensuring they do not miss hidden waterfalls, ancient temples, and unique local cultures that thrive beyond the popular tourist destinations.
Ultimately, whether you are a seasoned traveler or embarking on your first adventure, the Uttarakhand tourist place offerings are vast. The comprehensive Uttarakhand map makes it easier for individuals to plan their trips and discover both famous and obscure attractions, enhancing the overall enjoyment of this beautiful state.
The Importance of Maps in Ecological and Cultural Preservation
Maps serve as vital tools in the preservation of both ecological and cultural aspects of Uttarakhand. The state, renowned for its captivating landscapes and diverse ecosystems, benefits significantly from well-constructed maps that aid in conservation strategies. These maps provide critical information about biodiversity hotspots, allowing for efficient prioritization of regions that require protection and sustainable management. By analyzing the Uttarakhand map, conservationists can identify areas critical for maintaining the habitats of various species and implementing measures to curb environmental degradation.
In addition to ecological conservation, maps play a fundamental role in land-use planning within Uttarakhand. The state faces ongoing challenges related to urbanization and resource exploitation. By utilizing detailed geographic information systems (GIS) and topographical maps, planners and decision-makers can assess the impact of development projects on both the environment and local communities. Strategic land-use planning ensures that Uttarakhand’s travel places are developed responsibly, balancing economic growth with ecological sustainability and cultural preservation.
Maps also serve to engage local communities in the understanding and preservation of their cultural heritage. These artifacts depict significant landmarks, historical sites, and cultural narratives that provide the residents of Uttarakhand and visitors with a deeper appreciation of the region’s rich history. By involving local populations in the mapping process, it fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards their cultural heritage and landscapes. Furthermore, mapping demographic changes in Uttarakhand offers insights into migration patterns, community structures, and societal shifts, which are essential for tailoring sustainable development strategies.
Overall, the intersection of cartography with ecological and cultural preservation in Uttarakhand is paramount. As maps illuminate the intricate relationships between natural and cultural landscapes, they empower stakeholders to facilitate informed decision-making that promotes sustainability and resilience in the state.




Leave a Reply